Biopharmaceutical News Week 22
Acquisitions /mergers/joint-ventures
Chinese consortium buys US Ambrx
A consortium of Chinese healthcare business and funds will acquire US biotech Ambrx (San Diego, CA, USA) which abandoned its IPO last year. China Everbright’s healthcare fund, Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical Group, HOPU Investments and WuXi Pharma Tech have announced the deal without providing financial details. The acquisition will give WuXi access to Ambrx’s antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) technology as well as biologics development capabilities and expertise. Ambrx's pipeline includes ARX788, a site-specific ADC targeting Her2-positive breast cancer.
Cinven acquires Labco a diagnostic company for €1.2 Billion
Cinven (London, UK) a UK private equity fund has agreed to acquire Labco (Paris, France) a French diagnostic provider, which had postponed its IPO earlier this year, from a consortium of investors for around €1.2 billion. Labco operates medical diagnostic laboratories in France, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Belgium and the UK.
Rumors around the acquisition of Cellectis by Pfizer
In a rather depressed Paris stock market on Friday, Cellectis (Paris, France) traded at an increased value of 11.3% upon the rumor of a possible acquisition by Pfizer who had established a strategic collaboration based on Cellectis CAR-T technology platform and purchased 9.47% of the French company’s shares in June 2014.
Business
Sanofi enters cardiovascular agreement with NeuroVive
NeuroVive Pharmaceuticals (Lund, Sweden) announced that its Asia branch entered into an agreement with Sanofi to develop and commercialise CicloMulsion in South Korea. CicloMulsion is a cyclophilin inhibitor designed to treat reperfusion injury related to cardiovascular disease, which is also currently evaluated for the treatment of other acute heart and kidney injuries. Specific terms of the deal were not disclosed but NeuroVive Pharmaceuticals will be entitled to receive upfront and regulatory milestone fees as well as sales royalties.
…..and buys a priority review voucher from Retrophin for $245 million
Retrophin (San Diego, CA, USA) announced that it has agreed to sell its Rare Pediatric Disease Priority Voucher to Sanofi for $245 million. Under the term of the sale Sanofi will pay $150 million upon the signing of the contract and then two payments of $47.5million each in the two following years. The voucher, which Retrophin acquired from Askepion Pharmaceuticals, can be sold or transferred an unlimited number of times. It shortens the FDA's review for a New Drug Application (NDA) from ten to six months. This is the second time Sanofi uses this process to accelerate the US FDA approval for one of its drugs.
Rehnovia and Optivia enter into collaboration agreement
Rhenovia (Mulhouse, France) and Optivia Biotechnology (Menlo Park, CA, USA) announced their partnership agreement to provide customers cutting edge assays and services in transporter science and neuropharmacology for drug discovery. Terms of the agreement were not disclosed.
Juno signs collaboration deal with Editas worth $737 million
Juno Therapeutics (Seattle, WA, USA) has signed a deal with Editas Medicine (Cambridge, MA, USA) worth $737 million to develop new cancer treatments based on Editas’s “gene editing” technology in order to modify DNA to disable disease causing genes. Juno’s main focus is on advancing T cell based therapies for cancer patients. Editas will receive $25 million in upfront, $22 million in research funding and up to $690 million in future payments contingent to success and sales milestones.
Bayer announces corporate restructuring
The German company has announced that it will separate its life sciences businesses –Healthcare and CropScience- from its MaterialScience unit which will be demerged sometime next year. In order to do so Bayer is developing plans to reshape its corporate structure without staff reduction according to Management Board Chairman Dr. Marijn Dekkers.
Astra Zeneca ad Lilly collaborate on cancer drug combination
AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly agree to collaborate on a clinical trial to assess the safety and the efficacy of MEDI4736 in combination with Cyramza (ramucirumab) in patients with advances solid tumor.MEDI4736 is a monoclonal antibody known as a PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor. Binding to PD-L1 enables T cells to recognize and kill cancer cells. Cyramza is an antiangiogenic therapy known as a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) Receptor 2 antagonist. It inhibits the growth of tumors by restricting the formation of new blood vessels that fuel their expansion.
ArGEN-X and LEO form inflammation alliance
ArGEN-X (Breda, the Netherlands and Ghent, Belgium) and LEO Pharma (Ballerup, Denmark) have entered an alliance to investigate therapeutic treatment of inflammation-related skin diseases. Under the agreement ArGEN-X will provide LEO exclusive rights to a preclinical antibody that is investigated for the treatment of chronic inflammation. LEO shall pay an initial upfront of $4.5 million and potential milestones of more than $100 million and tiered royalties on sales of approved products.
Approval of drugs, vaccines, diagnostics and devices
Boehringer Ingelheim’s gets US FDA approval for its COPD drug
German Boehringer Ingelheim gets US FDA approval for its once-a day Stiolto Respimat (tiotropium and olodaterol) inhalation spray for the maintenance treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is not approved for the treatment of asthma. Tiotropium is a long-acting anticholinergic, the active ingredient in Spiriva, olodaterol is a long-acting beta2-agonist that complements the efficacy of Spiriva, with a fast onset of action that improves airflow.
…. and European Commission approval for Synjardy
Synjardy, a single pill containing empagliflozin and metformin, got European Commission approval for the treatment of glycemic control in adult type 2 diabetic patients. The product is co-developed with Eli Lilly.
European Commission recommends approval of Merck’s Keytruda
Following a similar recommendation for Bristol-Myers Squibb Opdivo last month, European Commission recommends the approval of Merck’s immune system boosting cancer drug Keytruda, also known as pembrolizumab for the treatment of melanoma. Both drugs are already approved by the US FDA.
US FDA approves two Valeant drugs for irritable bowel syndrome
The US FDA Food approved Viberzi known as eluxadoline, which Actavis obtained with its acquisition last year of Furiex Pharmaceuticals. The agency also approved Valeant's Xifaxan, also known as rifaximin, which the company acquired with its purchase earlier this year of Salix Pharmaceuticals. Both drugs are designed to treat diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D), a condition that can cause abdominal pain, bloating and diarrhea. Viberzi is a combination mu opioid receptor agonist and delta opioid receptor antagonist. It is designed to treat IBS-D while reducing the risk of constipation that can occur with other mu opioid receptor agonists, such as the anti-diarrhea drug Imodium. Xifaxan is an antibiotic that was approved in 2004 to treat traveler's diarrhea.
US FDA approves Pfizer’s Rapamune for rare lung disease
Pfizer got FDA approval for Rapamune, also known as sirolimus, for the treatment of lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) a rare progressive lung disease almost exclusively affecting women. The disorder is characterized by the overgrowth of abnormal smooth muscle-like cells in the lungs which leads to the formation of cysts and the destruction of normal lung tissue. Rapamune was originally approved back in 1999 as an immunosuppressive agent to prevent organ rejection in kidney transplant patients.
US FDA approves Roche Clostridium difficile test
Roche got FDA approval for its rapid test for Clostridium difficile developed on its cobas 4800 system. The test screens for a C. difficile gene in stool samples allowing physicians to rapidly make decisions to prevent the infection.
Drugs at clinical stage
US FDA grants ReNeuron fast track status for retinitis pigmentosa
ReNeuron (Guilford, UK) received US FDA fast track status for its human retinal progenitor cell therapy for the treatment of retinitis pigmentosa. Retinitis pigmentosa is a group of hereditary diseases of the eye that lead to progressive loss of sight due to cells in the retina becoming damaged and eventually dying. ReNeuron’s cell therapy candidate for retinitis pigmentosa has already been granted Orphan Drug Designation in both Europe and the US.
US FDA grants orphan status for Cerulean’s CRLX101 ovarian cancer drug
Cerulean Pharma (Cambridge, MA, USA) received orphan status designation for CRLX101, a nanoparticle-drug conjugate for the treatment of ovarian cancer. CRLX101 was designed to concentrate in tumors and slowly release its anti-cancer payload, camptothecin, inside tumor cells.![]()
Technology
Irish researchers developing technology to control diabetes
Research conducted in Ireland has led to the development of a gel containing clusters of pancreatic cells that can control glucose levels for up to five years when delivered through a minimally invasive injection procedure developed by Boston Scientific.
Eli Lilly supports insulin pen maker Companion Medical
Companion Medical (San Diego, CA, USA), a startup with a Bluetooth-enabled insulin pen and smartphone app, launched a Series B financing led by Eli Lilly. The investment amount was undisclosed but the move marks a step forward for Lilly into the world of drug delivery technology, for which the company is currently building an R&D center in Cambridge (MA, USA).
Medical Devices and Diagnosis News
Qiagen launches clinical bioinformatics platform for next-generation sequencing
Qiagen (Redwood, CA, USA and Hilden, Germany) announced the commercial launch of its Qiagen Clinical Insight (QCI) bioinformatics content and software platform for clinical testing to interpret and report on genomic variants identified in next-generation sequencing (NGS). QIAGEN demonstrated the QCI software at the following meetings ClinGen/DECIPHER Meeting (May 27-28, Washington D.C.), ASCO Annual Meeting (May 29-June 2, Chicago), and European Society of Human Genetics Conference (June 6-9, Glasgow).
Miscellaneous
Former Chinese healthcare official arrested on bribery charges
Wang Yu, the former leader of the federal agency in charge of managing medical device and drug clinical trial in China has been arrested for bribery. Prior to his retirement last month Wang headed the China’s Bureau of Medical Administration. Bloomberg reported that the government scrutiny about potential bribery is now shifting toward the medical device industry. Earlier this month, it reported on a preliminary investigation into imaging equipment manufacturers General Electric, Royal Philips and Siemens.
European Medicines Agency issues new guidelines on gene therapy
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is now seeking feed back on its new draft guideline aimed at clarifying the scientific evidence necessary to support the authorization of new gene therapies. EMA's draft Guideline on the quality, non-clinical and clinical aspects of gene therapy medicinal products is intended to answer questions that might arise during the development of a gene therapy. The draft guideline follows the order of the common technical document (CTD). The three main sections of the document outline considerations companies should take when designing non-clinical and clinical programs, as well as quality considerations that should be made in designing and manufacturing the product itself. Because gene therapies rely on a biological vector (viral, bacterial, cellular), companies must carefully consider the chosen vector's properties, and maintain "full documentation of the [vector’s] origin … history and biological characteristics." Additionally, EMA recommends vectors be "produced from well-characterized bacterial or virus seeds and/or cell banks," which in turn should be qualified and controlled to protect from contamination. For non-clinical programs, companies should pay careful attention to "potential in vivo effects of the transgene or recombinant nucleic acid sequences, the vector backbone and of the excipients including any carrier or support medical device employed." When designing non-clinical studies, companies should also ensure they have selected suitable end-points and control groups. Because of differences in gene therapies compared to traditional pharmaceutical substances, classical dose finding principles may not be applicable. In these cases, EMA says companies should instead establish a "minimal effective dose and a maximum tolerable dose.” For gene therapies using viral vectors, companies should evaluate the chosen vector for complications that may arise if patients have been previously exposed to the parent virus. Additionally, for therapies that require multiple doses over time, the product should be evaluated for immune response as well to ensure any developed response does not interfere with the product's therapeutic effect.
In 2014, 66% of the 41 new US Approved Drugs Earned Clearance through FDA Accelerated Approvals
In order to better understand the FDA factors needed to qualify for accelerated approvals: fast track designation, breakthrough designation, accelerated approval and priority review we are highlighting the FDA expedited review program below The FDA has previously offered programs to facilitate expedited drug development but with 2012’s FDA Safety and Innovation Act, those programs are beginning to make an impact. Last year, 66 percent of approved drugs earned clearance via an accelerated program. To qualify for an expedited pathway, the drug needs to treat what the FDA recognizes as a “serious condition.” According to the FDA, a serious condition is defined as any condition that, left untreated, will progress to a more serious one. The FDA also looks at factors such as survival and whether the condition has a serious negative impact on day-to-day functioning.
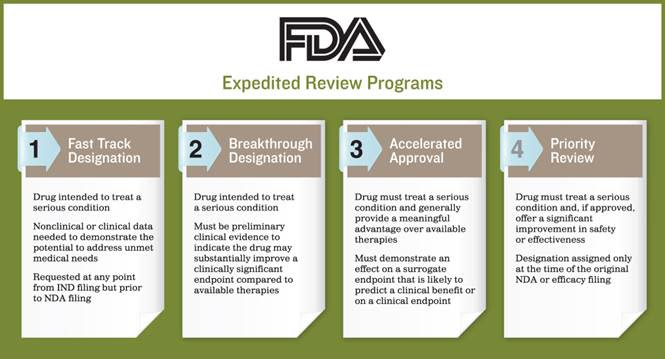
The FDA makes the following four expedited programs available to drug developers:
Fast Track Designation: To qualify, drug developers must provide non-clinical or clinical data that demonstrate the drug’s potential to address an unmet clinical need. If a treatment does exist, the drug may still be eligible as long as it provides a marked benefit for patients who are intolerant to the current therapy, delivers a significant improvement over the standard treatment, or produces a similar benefit with less toxicity. To reap the full advantage of the program, drug developers should submit requests prior to their pre-new drug application (NDA) meetings with the FDA.
Breakthrough Designation: To qualify for a Breakthrough Designation – the FDA’s newest expedited program – there must be preliminary clinical evidence indicating the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement compared to currently available therapies. Once accepted, drug developers gain access to intensive guidance from the FDA on how to best expedite the development process.
Accelerated Approval: Drugs falling under an Accelerated Approval pathway are required to offer a meaningful advantage over available therapies. The drug must also demonstrate a positive effect on the clinical endpoint before the patient reaches an irreversible stage of the treatment process.
Priority Review: Priority Review applies to drugs that, if approved, offer a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. The pathway guarantees a six-month review timeline for the marketing application, which under the standard pathway can take as long as 10 months.
Bio and Business Events
- IIR’s IN3 EuroMedtech 2015 on June 10-11 in Vienna (Austria)
- BIO International Convention on June 15-18 in Philadelphia (USA)
- Bio Taiwan 2015 on July 22-26 in Tapei (Taiwan)
- 3rd Annual Nordic Life Science Days Partnering Conference on September 9-10 in Stockholm (Sweden)
- BioPharm America 2015 on September 15-17 in Boston (USA)
Author: Jean-Claude Muller, Special Advisor at I&IR, jcm@btobioinnovation.com
Discover our services in Marketing & Business Development:
See All News
See other Biopharmaceutical News
see other Pharma & Biotech events in 2015
4
Last News
- Pétrole et semi-conducteurs : Une histoire qui se répète mais qui ne se ressemble pas.
- Oil and semiconductors: a story that repeats itself but is not the same.
- Stroke : An update
Events
News archives
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- November 2023
- September 2023
- July 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- August 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- October 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- September 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- January 2014
- November 2013
- September 2013
- July 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- March 2012





